Solutions
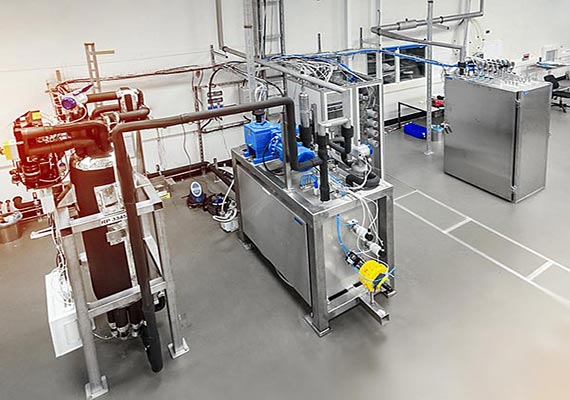
CERN relies on LEWA diaphragm pumps because the detector cooling circuit must not be contaminated with oil. Oil hardens under the influence of radiation from and then congest the cooling lines. At least for CO2 a compression cycle is not possible because no oil-free compressor for CO2 is available on the market.
LEWA pumps deliver an absolutely uniform flow which is necessary for a continuous and constant, two-phase cooling. The transition of the CO2 from the liquid in the gaseous state is used in order to dissipate heat. An important advantage of CO2 cooling: Due to the compression, the volume of the vaporized CO2 is very low, and tubes with a very small diameter of only two millimeters tubes can be used.
Another CO2 cooling system has a total power of 15 kW. For this plant, LEWA diaphragm metering pumps in remote head design with a cooling jacket are in use. The transmission of the displacement motion is performed by the liquid column contained in the connecting line. Thus, the remote head design keeps critical conditions away from the displacement system. In addition, heating of the CO2 or cooling of the oil is prevented, which would lead to the formation of gas bubbles. If the requirements change, the flow rate can be adjusted via the remote stroke adjustment.

Background

The European Organization for Nuclear Research, or CERN, founded in 1954, is dedicated to fundamental physical research. With approximately 2,500 employees from 22 member states, CERN is the world's largest particle physics research center. Currently more than 12,000 guest researchers from more than 100 countries conduct experiments in this large research center located in the Swiss canton of Geneva and in the French département of Ain.
Over the years, CERN has built several particle accelerators that accelerate various particles almost to the speed of light and make them collide. The organization commissioned its first particle accelerator, the Synchrocyclotron (SC), in 1957.
The Large Hadron Collider came into operation in 2008 and is currently the most important accelerator at CERN. By examining the trajectory of the particles, the results of decay, and the interactions between the particles, researchers can draw conclusions about the nature of matter and the origins of the universe. Due to the enormous technical effort required to create and operate the systems, CERN is operated and financed internationally.
Photos © CERN (2)
Industries
Pumps and Metering Systems for Other Industries
LEWA offers customized solutions and references for almost all industries in which processes require exact metering or the reliable conveyance of fluids. As specialists in fluid handling, we of course also have experience in areas outside of our key markets.
More DetailsProducts
LEWA ecoflow® diaphragm metering pump
LEWA ecoflow is the innovative and universal metering pump with DPS diaphragm protection system in a tried-and-tested modular system. Suitable for numerous applications, the ecoflow is our real all-around talent, relied on by customers from all industries.
More DetailsLEWA intellidrive® diaphragm metering pump
Design the suction and discharge strokes of the metering pump to meet your specific requirements! With LEWA intellidrive technology, you can model pumping characteristics individually.
More DetailsLEWA MAH, MBH, MLM Micro-metering pumps
Metering pumps for very small flow rates. An especially cost-effective solution when fluid components must be metered proportionally to a variable reference value.
More DetailsLEWA FC laboratory pumps
Metering pumps for very small flow rates. The FC micro-metering pumps for pressures up to 400 bar were developed specifically for laboratories and test centers.
More Details